|
|
|
Applications>>
Lasers for Medical Treatment |
| |
|
Lasers for Medical Treatment |
|
|
|
Laser used in medical field is the
important high-tech medical technology in this century,
laser medical treatment relates to all clinical disciplines,
such as ophthalmology, dermatology, surgery, dentistry, oncology, cancer, etc. Laser has a
breakthrough in medical treatment, and different
wavelengths suit for different therapeutic areas.
Changchun New Industries (CNI)
founded in 1996, is a manufacturer of solid-state and
diode laser systems. CNI laser features with high performance,
high reliability, and specifically designed for OEM, scientific,
medical,
industrial and instrumentation use. In addition, CNI lasers are
ISO-9001, FDA, CE, RoHS and JQA certified. CNI can provide
different lasers for medical treatment with free space and
pigtailed versions. Also the accessories related are
available for a total solution from customers. |
|
| |
|
Photodynamics
Therapy |
| |
|
 |
Photodynamic
therapy (PDT) is a new technique to treat tumor after
surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. It has the
advantages of small trauma, low toxicity, good
selectivity and high applicability.
The principle is to apply a drug
delivery method to give photosensitive drugs and then
irradiate the tumor site with a specific wavelength
light source at a certain time interval; using the
photosensitizing property of photosensitive drugs, the
photosensitive drugs selectively gathered in the tumor
tissue are activated to produce a series of chemical,
physical and biological light reactions to destroy the
tumor under the excitation of the light source. The
photosensitized drugs in the new generation photodynamic
therapy will transfer energy to the surrounding oxygen
to generate highly active monomorphic oxygen. The
monomorphic oxygen reacts with nearby biomolecules to
produce cytotoxicity and thus kill tumor cells.
Light source is one of
the necessary factors to ensure the smooth
implementation of photodynamic therapy. A good light
source should have the following characteristics: |
| |
|
Laser source
characteristics: |
|
■
The wavelength is near the absorption peak
of photosensitive drugs |
■
The light source has a certain amount of
tissue penetration during use |
|
■
The optical power can be adjusted |
■
The laser can be connect with optical fiber
to ensure more accurate treatment targeting points |
|
Common
wavelengths: |
|
405nm, 457nm,
532nm, 561nm, 577nm, 589nm,
635nm,
808nm,
Multi-wavelength laser,
etc. |
|
Other
wavelengths can be customized.
|
|
Accessories: |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Fiber Patch Cables |
Beam Shutter |
Power Meter
|
Laser
Goggles |
Portable
variable
attenuator |
| |
|
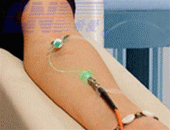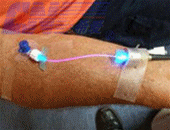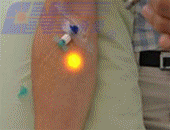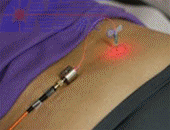
Laser Therapy |
| |
|
 |
|
Areas of
application: |
|
|
■
External laser therapy |
■
Interstitial laser therapy |
|
■
Intra-articular laser therapy |
■
Intravenous laser therapy |
|
■ Pain
therapy |
■
Photodynamic therapy |
|
Common
wavelengths: |
|
|
447nm,
532 nm,
589 nm,
655 nm,
810 nm... |
With free
space or fiber coupling output option, usually the
power is 5~100 mW for 447 nm blue laser, 5~50 mW for
532 nm green laser and 589 nm yellow laser, both
power and frequency can be adjusted individually.
|
|
|
|
Laser for Ophthalmology |
|
|
|
|
 |
Eyes are the most
sophisticated, one of the most important organs. Also
eyes are very fragile and vulnerable. Once the eyeball
appears lesion, it is difficult to remove the lesion
safely by normal surgery. Laser treatment for fundus
diseases is so effective that it has even become the
first choice for certain fundus diseases. One of the
more clinically used laser treatment devices is the
multi-wavelength fundus laser. It integrates three
wavelengths of laser light - yellow, red and green in
one, and can instantly switch between red, green and
yellow wavelengths without time lag. It can meet the
laser treatment of various fundus diseases, with the
characteristics of simple, rapid, minimally invasive and
effective, and is a technology that cannot be replaced
by other treatment methods, and is globally recognized
as the "gold standard" for laser treatment of fundus
diseases.
Fundus tissues have different absorption rates for
different wavelengths of the laser. Clinically, using
these characteristics, different colors of lasers can be
selected to treat different diseases, for example:
| |
|
1. Melanin and
hemoglobin have strong absorption of
green light,
which can be used to select green light for
laser photocoagulation. |
|
2.The spot area
does not absorb yellow
light, so you can choose to treat the
area around the macula to avoid visual
impairment caused by accidental laser injury
to the macula. |
|
3. The
absorption rate of hemoglobin to
red light is
low, so red light has a high penetration of
blood. For patients with vitreous
hemorrhage, red light can be selected for
fundus photocoagulation. |
|
Areas of
application: |
|
|
■ Retinal photocoagulation
|
■
Trabecular angioplasty |
|
■ Iridotomy |
■
Lamellar keratoplasty |
|
■
Cataract surgery |
■
Vitreous Lysis |
|
Common
wavelengths: |
|
|
532 nm,
561nm,
577nm,
635nm,
671 nm,
810 nm,
980 nm,
1064 nm,
1320 nm,
Multi-wavelength laser |
Normally
several millijoules are needed for pulsed laser, such
as 2 mJ for 532 nm laser and 10mJ for 1064 nm laser.
The power is around several watts such as 2 W, 3 W for
532 nm green laser.
|
|
|
|
|
Laser for Dermatology |
|
|
|
|
 |
Laser for dermatology
treatment has also made rapid progress over the past decade. In
Europe, America, Japan and other countries, dermatologic surgery
uses non-intervention type of treatment to achieve a good
therapeutic purposes, instead of traditional surgery,
transurethral resection, skin grafting and other technologies.
Currently, the laser has been widely used in in varieties of
skin and beauty items.
|
Areas of
application: |
|
|
■
Vascular lesions |
■
Pigmented lesions |
|
■
Onychomycosis |
■
Tattoo removal |
|
■ Hair
removal |
■
Laser resurfacing |
|
Common
wavelengths: |
|
|
532 nm, 593 nm,
650 nm, 750 nm, 808 nm, 980 nm, 1064 nm,
1085 nm, 1320 nm, 1342 nm, 1550 nm... |
|
Normally single
pulse energy for pulsed laser needs hundreds
to thousands millijoules such as 400 mJ for
532 nm, 800/ 1600 mJ for 1064 nm with several
hertz Rep.rate. |
|
CNI lasers: |
|
LPS-L-532/ 1~450 mJ/
1~10 Hz |
LPS-M-1064/ 1~10 J/ 1~20
Hz |
|
LPS-L-1064/ 350~1000 mJ/
1~10 Hz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Laser for Surgery |
|
|
|
|
 |
Laser surgery uses laser light to remove
diseased tissues or treat bleeding blood
vessels. Laser surgery may also be used to
remove wrinkles, sunspots, tattoos, or
birthmarks.
|
Areas of
application: |
|
|
■
Oncology (cancer treatment) |
■
Varicose veins |
|
■
Gallstones |
■
Lithotripsy |
|
■
Urological surgery |
■
Gynecological surgery |
|
Common
wavelengths: |
|
|
447nm,
532 nm,
561nm,
577nm,
635nm,
810 nm,
980 nm,
1064 nm,
1320 nm,
1470 nm... |
|
Especially the
double pulsed frequency doubling laser type
with 532 nm and 1064 nm combined for 120 mJ/
160 mJ of single pulse energy, 240/ 320 mJ
of double pulse energy. |
|
|
|
|
|
Lasers Related |
|
|
|
YL-455/
1~25W |
YL-520/
1~6W |
YL-635/
1~3W
|
|
YL-F-980/
808/ 520/
455/
23W
|
YL-F-980/
808/ 635/
455/
23W |
YL-S-980/
808/ 635/
520/ 455/
24W |
|
|
Wavelengths:
360 nm,
375 nm,
405 nm,
447 nm,
455 nm,
457 nm,
465 nm,
473 nm,
488 nm,
514.5 nm,
520 nm,
532 nm,
543 nm,
556 nm,
561 nm,
577 nm,
589 nm,
593 nm,
635 nm,
650 nm,
665 nm,
671 nm,
690 nm,
750 nm,
808 nm,
810 nm,
830 nm,
885 nm,
980 nm,
1040 nm,
1064 nm,
1320 nm,
1342 nm,
2096 nm,
2200 nm,
2796 nm,
etc. |
|
| |
|
Related Research of CNI
Laser in
Medicine from Customers |
|
(1)
Inhibition of NF-κB in Tumor Cells
Exacerbates Immune Cell Activation Following Photodynamic
Therapy
(Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19960-19977;
doi:10.3390/ijms160819960) (CNI-671 nm)
(2) An in vitro study of the
photodynamic effect of rose bengal on Trichophyton rubrum
(J. Biophotonics 7, No. 6, 410–417 (2014) / DOI
10.1002/jbio.201200168) (CNI-532 nm)
(3) Local Field Enhanced Au/CuS
Nanocomposites as Efficient Photothermal Transducer Agents for
Cancer Treatment
(Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology Vol. 8,
883–890, 2012) (CNI-980 nm)
(4) Low-power photodynamic
therapy induces survival signaling in perihilar
cholangiocarcinoma cells
(Weijer et al. BMC Cancer (2015) 15:1014/ DOI
10.1186/s12885-015-1994-2) (CNI-671 nm)
(5) Toward New Engagement
Paradigms For Intraocular Lenses: Light-Initiated Bonding of
Capsular Bag to Lens Materials
(Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2015;56:4249–4256.
DOI:10.1167/ iovs.15-17070) (CNI-532 nm)
(6) Elimination of
epithelial-like and mesenchymal-like breast cancer stem cells to
inhibit metastasis following nanoparticle-mediated
photothermal therapy
(H.J. Paholak et al. / Biomaterials 104 (2016)
145e157) (CNI-885 nm)
(7) Modelling and
characterization of Photothermal effects assisted with Gold
Nanorods in ex-vivo samples and in a murine model
(Proc. of SPIE Vol. 7901 79010D-2. DOI:
10.1117/12.875706) (CNI-808 nm)
(8) Photobleaching and
phototoxicity of KillerRed in tumor spheroids induced by
continuous wave and pulsed laser illumination
(J.
Biophotonics 1–9 (2015) / DOI 10.1002/jbio.201400130) (CNI-593 nm)
|
| |
|